Genetic Carrier Screening
Genetic Carrier Screening is DNA-based testing to identify individuals or couples at increased risk of having children with severe inherited genetic disorders, performed in order to inform reproductive decision-making.
Why genetic carrier screening
Genomic Diagnostics’ genetic carrier screening tests for three of the most common inherited genetic conditions: cystic fibrosis (CF), fragile X syndrome (FXS) and spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
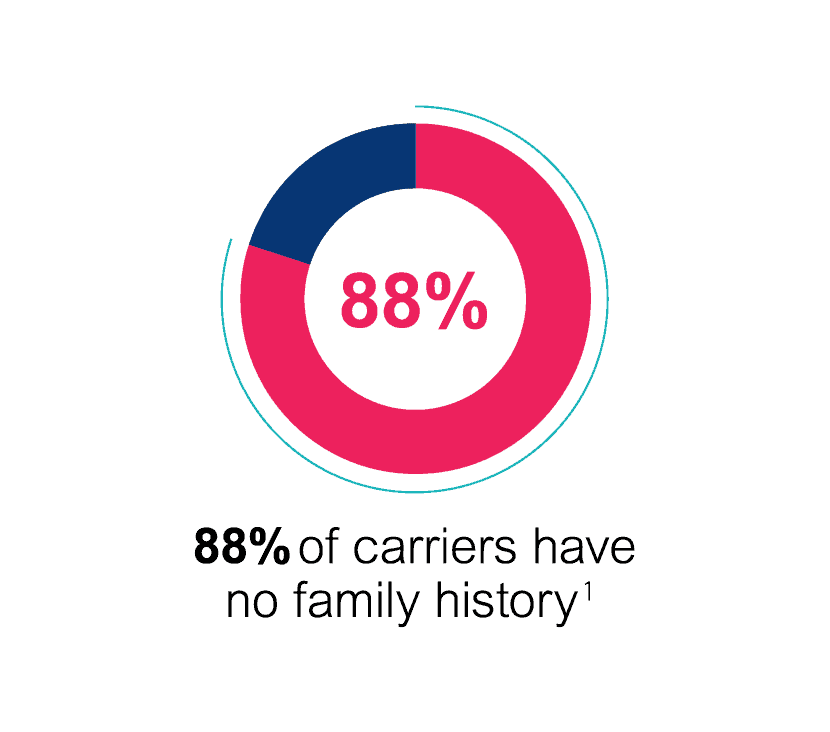
One in 20 Australians will be a carrier for at least one of these conditions, however most will have no family history of disease1. This is due to the relatively rare nature of the conditions and their inheritance patterns, either autosomal recessive or X-linked.
Carrier screening for CF, FXS and SMA is now funded by Medicare and should be offered to those considering pregnancy or in their first trimester

Why screening is important
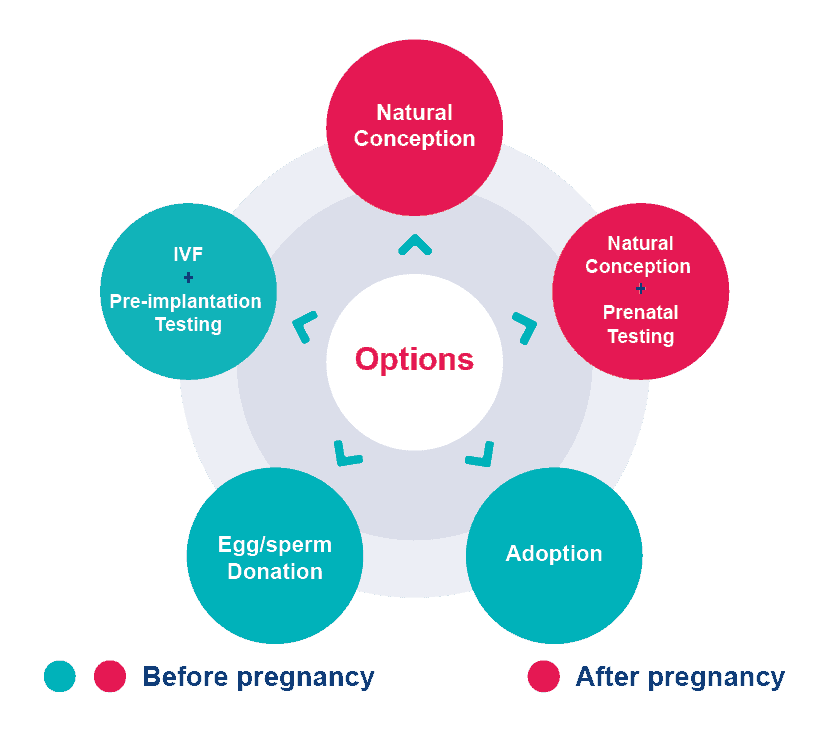
Genetic carrier screening helps to inform reproductive decision-making.
It gives carrier couples (where both partners are carriers for CF or SMA or the female partner is a carrier for FXS) the opportunity to consider a range of reproductive options.
When to offer screening
RANZCOG recommends that information on carrier screening be offered to all women planning a pregnancy or in the first trimester of pregnancy.2 This includes screening for CF, FXS and SMA. The genetic carrier screening test can be easily added as part of a patient’s routine antenatal blood screening.
There is global consensus that genetic carrier screening is best performed before pregnancy. This gives your patients the widest range of reproductive choices and more time to make important decisions.
Carrier screening can still be offered in early pregnancy, although options will be more limited and time-sensitive.
The recommended screening pathway is to test the female partner first, followed by the male partner if the female is identified as a carrier for CF or SMA.
Ordering genetic carrier screening
There are only three simple steps to ordering genetic carrier screening.

2. Sample collection
• Patient attends collection centre with their signed request form
• Blood is collected
• Genetic carrier screening is performed
1. Patient Consultation
- Discuss carrier screening with your patient as recommended by clinical guidelines
- Order Genetic carrier screening on a standard request form, noting any family history or pregnancy, and if the reproductive partner is a known carrier
2. Sample collection
- Patient attends collection centre with their signed request form
- Blood is collected
- Genetic Carrier Screening is performed

3. Result discussion
- Results are delivered to you by your preferred method
- Genetic counselling is offered for couples who are identified as carriers
Genetic conditions screened
CF, SMA and FXS can have devastating effects on life-expectancy and quality of life. The combined affected pregnancy rate for these disorders is equivalent to the population risk of having a child with Down syndrome.
| Cystic Fibrosis | Fragile X Syndrome | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Most common inherited disorder in Caucasians | Most common form of inherited intellectual disability | Most common genetic cause of mortality in children under two |
| Carrier Risk | 1 in 25 | 1 in 200 | 1 in 35 |
| People with the Condition | 1 in 2,500 | 1 in 3,600 males 1 in 6,000 females | 1 in 10,000 |
| Testing Approach | Testing for the 50 most common CFTR variants that are associated with more than 95% of CF cases | Testing for triplet repeat expansions in the FMR1 gene that are associated with more than 99% of FXS cases | Testing for the SMN1 gene deletion that is associated with more than 95% of SMA cases |
| Inheritance | Autosomal recessive; both parents must be carriers to have an affected child | X-linked; the mother must be a carrier to have an affected child | Autosomal recessive; both parents must be carriers to have an affected child |
Accuracy of screening results
Genetic carrier screening tests for the most common genetic changes associated with CF, SMA and FXS.
The assay can detect:
- >95% of cystic fibrosis carriers
- >99% of fragile X carriers
- >95% of spinal muscular atrophy carriers
The tests used for GCS are highly accurate diagnostic tests that reliably identify carriers for these conditions. However, genetic carrier screening cannot identify a small percentage of carriers (1-5%) because some very rare genetic variants cannot be detected by the test.
Genomic Diagnostics offers two genetic carrier screening options.
MBS*
Genetic Carrier Screening
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Fragile X
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy
*Medicare Criteria Apply
Results available within 10 business days.
$579
Myriad Foresight Expanded Carrier Screening
- Over 175 conditions
- Pre and post genetic counselling included
Results available within 10-15 business days from receipt in our overseas laboratory.
Genetic carrier screening resources
We offer genetic counselling free of charge for all carrier couples. This professional service provides information about the condition and enables in-depth discussions about a range of options.
Genetic carrier screening for CF, FXS and SMA is now listed on the Medicare Benefits Schedule.
Medicare Item 73451 – Female who is pregnant or planning pregnancy
One test per lifetime for a patient who is pregnant or planning pregnancy, to identify carrier status for pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in the following genes, for the purpose of determining reproductive risk of CF, SMA or FXS: (a) CFTR (b) SMN1 (c) FMR1
Medicare Item – 73452 – Reproductive partner of a carrier
One test per condition per lifetime for the reproductive partner of a patient who has been found to be a carrier of a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in the CFTR or SMN1 gene identified by testing under item 73451, for the purpose of determining the couple’s reproductive risk of CF or SMA.
DNA can be extracted from a range of sample types, including blood and saliva. We choose blood samples for Genetic Carrier Screening as this provides the highest quality DNA for testing, and ensures a quick and reliable result. Using blood also enables GCS to be easily added as part of a patient’s routine antenatal blood screening.
Resources
Select your state:
Leading the way to improved health
results in the shortest turnaround time.



